ACLU Again Cowardly Abstains From an Online Censorship Controversy: This Time Over BLM
The once-principled group issues P.R.-scripted excuses or engages in obfuscation to avoid taking stances that would offend its liberal donor base.

Enormous sums of money have poured into racial justice groups since the May, 2020 murder of George Floyd by a Minneapolis Police Department officer. “The foundation widely seen as a steward of the Black Lives Matter movement says it took in just over $90 million last year,” according to a February Associated Press review, while at least $5 billion was raised by groups associated with that cause in the first two months alone following Floyd's death.
Two weeks after the Floyd killing, The New York Times said that the “money has come in so fast and so unexpectedly that some groups even began to turn away and redirect donors elsewhere,” while “others said they still could not yet account for how much had arrived.” Propelled by the emotions and nationwide protest movements that emerged last summer, corporations, oligarchs, celebrities and the general public opened their wallets and began pouring money into BLM coffers and have not stopped doing so.
Where that money has gone has been the topic of numerous media investigations as well as concerns expressed by racial justice advocates. AP noted that BLM's sharing of financial data in February “marks the first time in the movement’s nearly eight-year history that BLM leaders have revealed a detailed look at their finances.” That newfound transparency was prompted by what AP called “longstanding tensions boil[ing] over between some of the movement’s grassroots organizers and national leaders — the former went public last fall with grievances about financial transparency, decision-making and accountability."
In December, ten local BLM chapters severed ties with the national group amidst questions and suspicions over the handling of activities and finances by one of its co-founders, Patrisse Cullors, who had assumed the title of Executive Director. On April 10, The New York Post published an exposé on what it called Cullors’ “million-dollar real estate buying binge.” The paper noted that as protests were unfolding around the country, the BLM official was “snagging four high-end homes for $3.2 million in the US alone, according to property records,” including a California property valued at $1.4 million. The article also revealed that the self-described Marxist and her partner “were spotted in the Bahamas looking for a unit at the Albany,” an “elite enclave laid out on 600 oceanside acres,” which “features a private marina and designer golf course.” The Post included photos of several of the properties obtained from public real estate listings.
In an interview about that Post story with Marc Lamont Hill, Cullors — except saying she has not visited the Bahamas since the age of 15 — did not deny the accuracy of the reporting, but instead justified her real estate acquisitions. She denied she had taken a salary from the BLM group, pointing to other income she earns as a professor, author, and a YouTube content creator as the source of this sudden outburst of real estate purchases. She denounced the Post reporting as "frankly racist, and sexist.”
So that seems like a perfectly healthy cycle for covering a controversy, obviously in the public interest. In the wake of concerns from activists about where this massive amount of BLM money has gone, The New York Post did its job of unearthing the splurge of real estate acquisitions by the person who controls and directs BLM's budget and who has been a target of accusations and suspicions from activists. Cullors then had the opportunity to publicly provide her side of the story concerning her aggressive and ample financial investments.
But then something quite unhealthy and unusual occurred. Five days after publication of that Post article, the Substack journalists Shant Mesrobian and Zaid Jilani reported that Facebook was banning the sharing of that article worldwide on its platform — similar to what Twitter and Facebook did in the weeks leading up to the 2020 election to The New York Post's reporting on the Biden family's business dealings in China and Ukraine. The Substack reporters noted that Facebook ultimately confirmed the worldwide ban of the Post's reporting to The New York Times’ media reporter Ben Smith, justifying it on the ground that the article “revealed personal details about [Cullors] and her residence in violation of Facebook’s community standards.”

In his weekly New York Times Sunday night media column, Smith returned to this subject. When a Facebook lawyer justified the censorship by citing an alleged policy that the tech monopoly will ban any “article [which] shows your home or apartment, says what city you’re in and you don’t like it,” Smith expressed extreme skepticism:
The policy sounds crazy because it could apply to dozens, if not hundreds, of news articles every day — indeed, to a staple of reporting for generations that has included Michael Bloomberg’s expansion of his townhouse in 2009 and the comings and goings of the Hamptons elites. Alex Rodriguez doesn’t like a story that includes a photo of him and his former fiancée, Jennifer Lopez, smiling in front of his house? Delete it. Donald Trump is annoyed about a story that includes a photo of him outside his suite at Mar-a-Lago? Gone. Facebook’s hands, the lawyer told me, are tied by its own policies.
Presumably, the only reason this doesn’t happen constantly is because nobody knows about the policy. But now you do!
Smith was additionally disturbed that Facebook was, in essence, overriding the editorial judgment of news outlets, which grapple every day with how to strike the balance between ensuring the public knows of information in the public interest and protecting a person's right to privacy. For obvious reasons, public figures and organizations — which both BLM and Cullors undoubtedly are — are deemed to have a lower expectation of privacy when it comes to what is newsworthy. That is why, for example, the extramarital affairs of Donald Trump or Bill Clinton are deemed newsworthy whereas, outside of the dead-but-returning Gawker sewer, the sex lives of private citizens are not. Yet Facebook accords no deference to the editorial judgments even of the most established media outlets. Instead, they told Smith, “Facebook alone decides.”
Whatever one’s views are on this particular censorship controversy, there is no doubt that it is part of the highly consequential debate over online free speech and the ability of monopolies like Facebook to control the dissemination of news and the boundaries of political discourse and debate. That is why Smith devoted his weekly column to it. And yet, when Smith approached the standard free speech advocacy groups for comment on this story, virtually none was willing to speak up. “Facebook’s usual critics have been strikingly silent as the company has extended its purview over speech into day-to-day editorial calls,” he wrote.
Among those groups which insisted that it would not comment on Facebook's censorship of the Post's BLM story was the vaunted, brave and deeply principled free speech organization, the American Civil Liberties Union. “We don’t have anyone who is closely plugged into that situation right now so we don’t have anything to say at this point in time,” emailed Aaron Madrid Aksoz, an ACLU spokesman. Smith said “the only criticism he could obtain came from the News Media Alliance, the old newspaper lobby, whose chief executive, David Chavern, called blocking The Post’s link ‘completely arbitrary’ and noted that ‘Facebook and Google stand between publishers and their audiences and determine how and whether news content is seen.’”
How is it possible that the ACLU is all but invisible on one of the central free speech debates of our time: namely, how much censorship should Silicon Valley tech monopolists be imposing on our political speech? As someone who intensively reports on these controversies, I can barely remember any time when the ACLU spoke up loudly on any of these censorship debates, let alone assumed the central role that any civil liberties group with any integrity would, by definition, assume on this growing controversy.
In lieu of the traditional, iconic and organization-defining willingness — eagerness — of the ACLU to defend free speech precisely when it has been most controversial and upsetting to liberals, what we now get instead are cowardly, P.R.-consultant-scripted excuses for staying as far away as possible: “We don’t have anyone who is closely plugged into that situation right now so we don’t have anything to say at this point in time.” That sounds like something Marco Rubio's office says when asked about a Trump tweet or that a corporate headquarters would say to avoid an inflammatory controversy, not the reaction of a stalwart civil liberties group to a publicly debated act of political censorship.
In this particular case, it is not difficult to understand the cause of the ACLU's silence. They obviously cannot defend Facebook's censorship — affirmatively defending the stifling of political speech is, at least for now, still a bridge too far for the group — but they are petrified of saying anything that might seem even remotely critical of, let alone adversarial to, BLM activists and organizations. That is because BLM is one of the most cherished left-liberal causes, and the ACLU now relies almost entirely on donations and grants from those who have standard left-liberal politics and want and expect the ACLU to advance that ideological and partisan agenda above its nonpartisan civil liberties principles. Criticizing BLM is a third rail in left-liberal political circles, which is where the ACLU now resides almost entirely, and thus it again cowers in silence as another online act of censorship which advances political liberalism emerges. Indeed, BLM is an organization which the ACLU frequently champions:
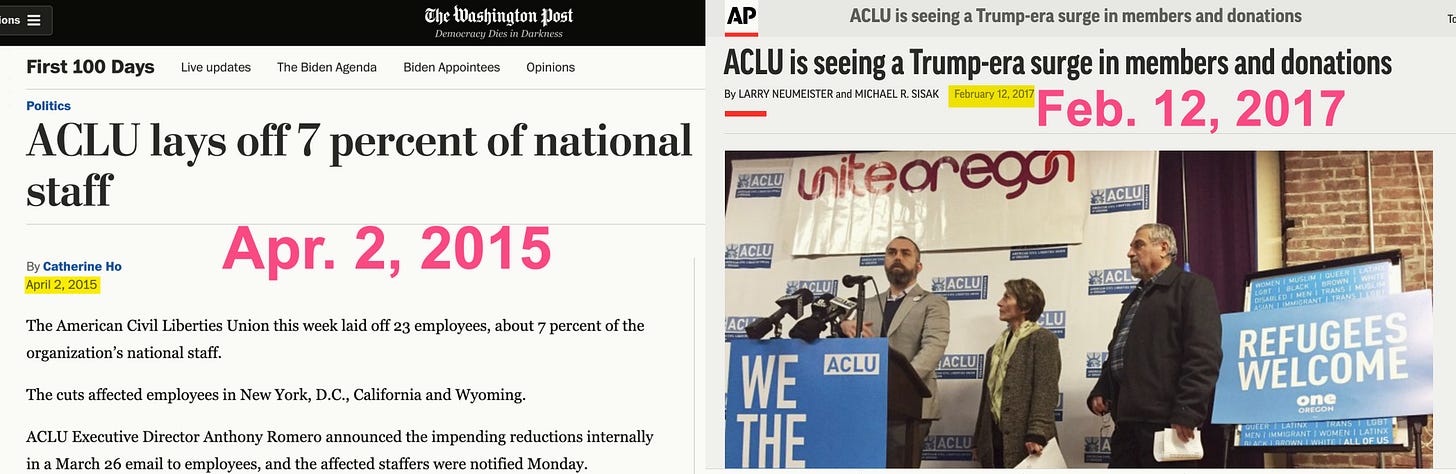
Like so many liberal-left media outlets and advocacy groups, the ACLU was suffering financially before they were saved and then enriched beyond their wildest dreams by Donald Trump and the #Resistance movement he spawned. “The American Civil Liberties Union this week laid off 23 employees, about 7 percent of the organization’s national staff,” announced The Washington Post in April, 2015. But in the Trump era, the money flowed in almost as quickly and furiously as post-Floyd money to BLM. In February, 2017, said AP, the group “is suddenly awash in donations and new members as it does battle with President Donald Trump over the extent of his constitutional authority, with nearly $80 million in online contributions alone pouring in since the election.” So that is the donor base it now serves.
The ACLU's we-know-nothing routine for abstaining from commenting on Facebook's censorship of the BLM article is, for so many reasons, preposterous. The group funds what it calls its Speech, Privacy, and Technology Project, and some of its best lawyers oversee it. Clearly they focus on these issues. And the ACLU in general has taken a firm and borderline-absolutist position against online censorship by Silicon Valley monopolies: principles whose application to this particular case would be easy and obvious. The ACLU has a section of its website devoted to “Internet Speech,” and its position on such matters is stated explicitly:
The ACLU believes in an uncensored Internet, a vast free-speech zone deserving at least as much First Amendment protection as that afforded to traditional media such as books, newspapers, and magazines….The ACLU has been at the forefront of protecting online freedom of expression in its myriad forms. We brought the first case in which the U.S. Supreme Court declared speech on the Internet equally worthy of the First Amendment’s historical protections.
In a July, 2018 article published on the group's site entitled “Facebook Shouldn't Censor Offensive Speech,” the group praised Facebook CEO Mark Zuckerberg's controversial pledge “to keep Facebook from diving deeper into the business of censorship” as “the right call.”
Unlike in response to the BLM controversy, the ACLU had no trouble back then recognizing that “what's at stake here is the ability of one platform that serves as a forum for the speech of billions of people to use its enormous power to censor speech on the basis of its own determinations of what is true, what is hateful, and what is offensive.” The ACLU's stated policy on these controversies could not have been clearer: “given Facebook’s nearly unparalleled status as a forum for political speech and debate, it should not take down anything but unlawful speech, like incitement to violence.” In light of that principle, how is it remotely hard to denounce Facebook's censorship of the Post's article given that it does not even arguably fall within the scope of those narrow exceptions?
Because the ACLU still employs a few old-school civil libertarians among its hundreds of lawyers and staff, those employees manage to do work and express views that are consistent with the ACLU's old-school civil liberties agenda even when contrary to the interests of liberal politics. But the tactics used by the ACLU in those cases to downplay or hide those aberrations are as transparent as they are craven.
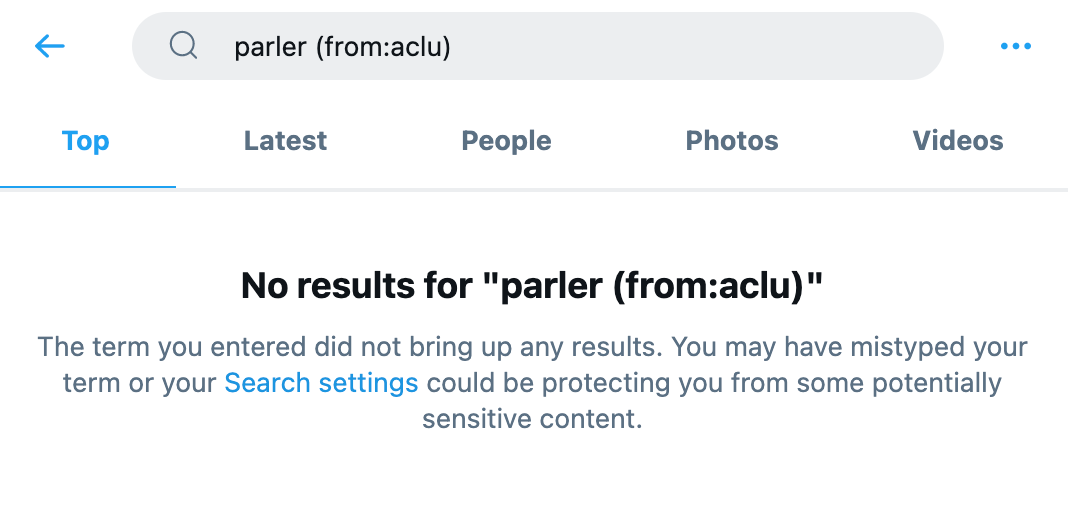
When three Silicon Valley monopolies united to remove the social media app Parler from the internet in January, 2021 after influential Democratic lawmakers demanded it — one of the most brute acts of monopolistic censorship yet — an ACLU lawyer, Ben Wizner, was cited in The New York Times as labelling Parler's destruction “troubling,” telling the paper: “I think we should recognize the importance of neutrality when we’re talking about the infrastructure of the internet.” But on the ACLU's highly active and influential Twitter account — the group's primary platform for promoting its work, expressing its views, and soliciting donations, where it has two million followers and often tweets up to fifty times a day — the group said absolutely nothing about the removal of an entire social media app from the internet:
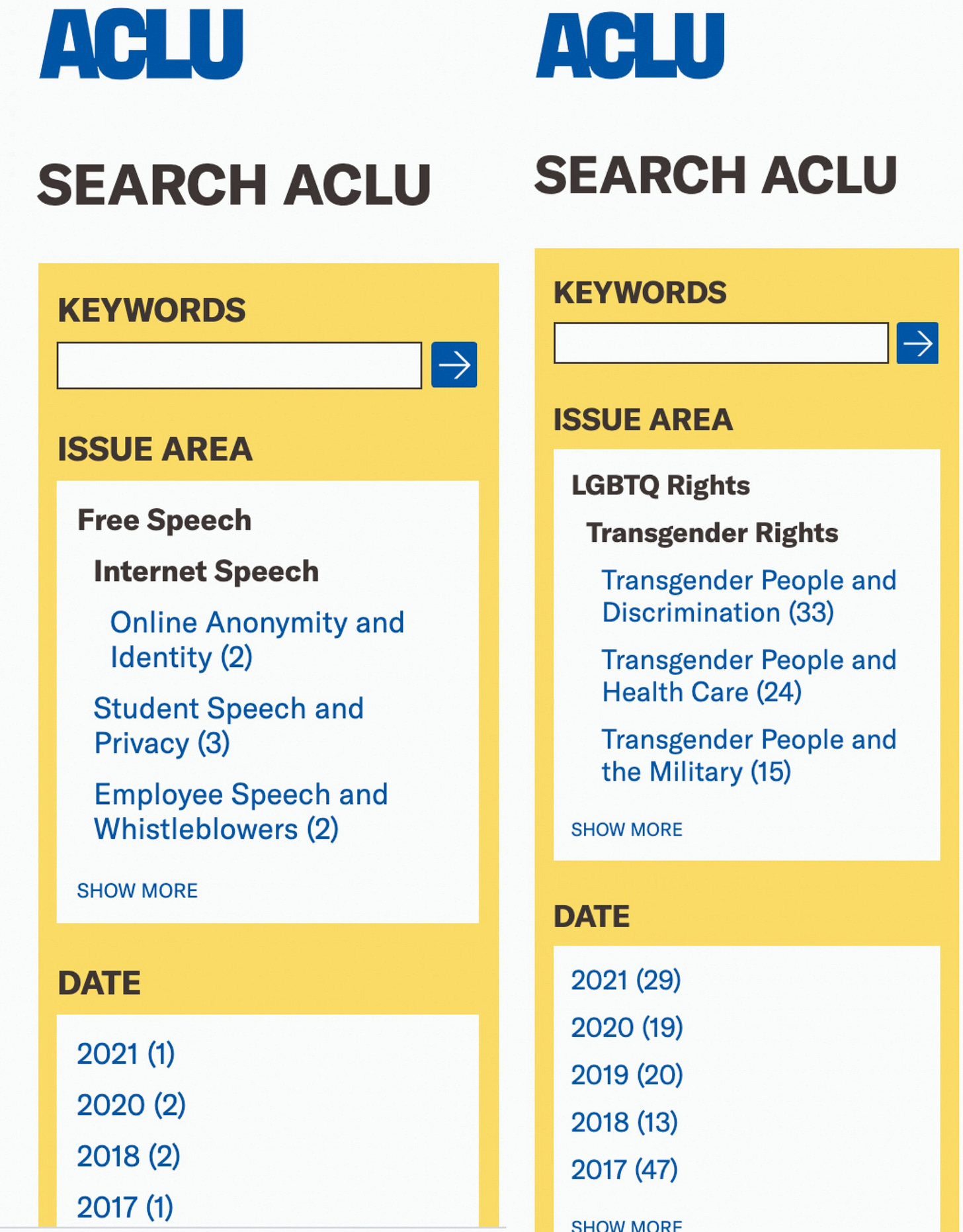
Indeed, the ACLU — outside of a few token, hidden statements — has chosen to play at most a minor role in the key free speech controversies of the day, ones focusing on such weighty matters as internet freedom and online censorship over our political debates by Silicon Valley monopolies. Over the last four years, as Facebook's censorship has expanded rapidly, the ACLU has said little to nothing about it — including remaining in utter silence about the extraordinary decision to censor pre-election reporting on Hunter Biden's laptop and what it revealed about Joe Biden's business dealings. Last month, Substack reporter Michael Tracey reviewed the ACLU's prior 100 tweets and found that 63 of them were about trans issues while a grand total of one was about free speech and none about due process. A comparison of the number of ACLU statements on online censorship controversies to its manifestations on trans issues similarly reveals a fixation on the latter with very little interest in the former:
It goes without saying that the ACLU has every right to devote a huge bulk of its institutional resources and public advocacy to the cause of trans equality if it chooses to do so. But what that reveals is that the group is becoming exactly what its leaders always vowed it would never be: just another garden-variety liberal political advocacy group. After all, there is no shortage of extremely well-financed LGBT groups doing the same advocacy on trans issues. Those LGBT groups shifted their focus almost entirely to trans issues when they won the entire agenda of gay and lesbian equality with the Supreme Court's 2015 legalization of same-sex marriage in all fifty states, and supporting trans rights is the mainstream, standard view of Democratic Party leaders and liberal activists.
The ACLU's refusal to engage with growing online censorship is baffling even from the perspective of its liberal politics given that radical leftists are increasingly (and predictably) the targets of tech censorship alongside anti-establishment right-wing voices. Just yesterday, the highly popular trans YouTube host Natalie Wynn of Contrapoints complained that one of her past episodes had just been demonetized and urged: “Free speech should be reclaimed as an essential leftist issue. We should not surrender the most fundamental civil right to Google LLC in the name of deplatforming rightists and curtailing harassment.” Wynn's last video, rebutting the views of J.K. Rowling on trans issues, featured Wynn's list of the telltale signs of “indirect bigotry” toward trans people, and she included "free speech advocacy,” but — as happens to so many people — Wynn has apparently reconsidered that view and has discovered the centrality of free speech values now that her own speech is targeted. But agitating for more online political censorship still remains a cause deeply popular among establishment liberals, further explaining the ACLU's reluctance to involve itself in these controversies on the side of free expression.
What always distinguished the ACLU in the past — and what gave it credibility with judges in courtrooms — was its devotion to and focus on non-partisan free speech, free press and due process causes that were too unpopular or controversial for other groups to touch, particularly liberal groups who could not afford to offend the political sensibilities of Democrats. There are still some isolated occasions when the ACLU does such things — such as when it spoke up in defense of the NRA against New York Governor Andrew Cuomo's efforts to target the group with destruction or when the ACLU recently denounced parts of the Democrats’ H.R.1 “reforms”— but the ACLU largely hides those exceptions on its most popular public platforms, and they are becoming increasingly rare.
And now we have arrived at the truly depressing and tawdry place where the ACLU is afraid to apply its long-stated principles to denounce Facebook's censorship because the censorship in question happened to be an article that reflected poorly on the sacred-among-liberals BLM group. In the place of brave lawyers and activists defending the constitutional rights and civil liberties even of those people and groups most despised, we have instead a corporate spokesman emailing The New York Times with excuses about why it cannot and will not speak up about a major censorship controversy that has been brewing for two weeks. In that decline one finds the ACLU's sorry trajectory from stalwart civil liberties group into a lavishly funded arm of the Democratic Party's liberal political wing.







After being a proud and card carrying ACLU member for 20 years, I cancelled my membership when ACLU failed to stand up to prosecution of Assange.
Sorry Glenn, George Floyd was not murdered by the “Minneapolis Police Department.” He was murdered by Derek Chauvin, a Minneapolis police officer. By saying what you did, you 1) impugned all of the men and women of that department, 2) lessen Chauvin’s personal culpability, 3) play into the narrative of institutional/ structural racism. You should edit that.